Introduction
Multidimensional arrays in Java allow you to store data in a table-like structure, making them essential for matrix operations, grids, and complex datasets. They are widely used in game development, mathematical computations, and data modeling.
In Java, multidimensional arrays are essentially arrays of arrays, giving you the flexibility to create both rectangular and jagged arrays.
Declaring Multidimensional Arrays
You can declare a 2D array as:
int[][] matrix;
For 3D arrays:
int[][][] cube;
Initializing Multidimensional Arrays
You can initialize during declaration:
int[][] matrix = ({1, 2, 3}, {4, 5, 6}, {8, 9, 7});
Or dynamically:
int[][] matrix = new int[3][3]; // 3x3 matrix
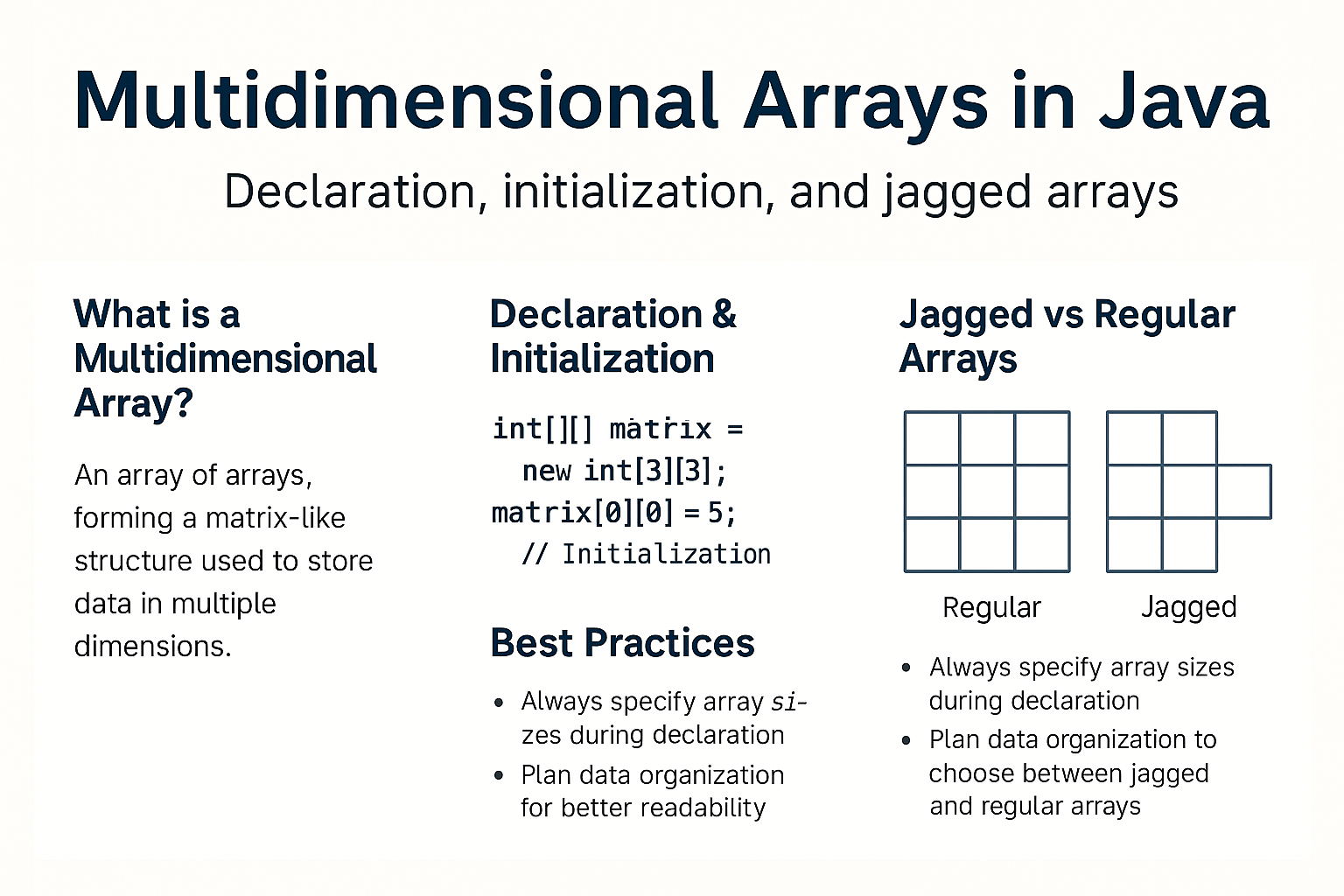
Jagged Arrays in Java
Jagged arrays are arrays of arrays with varying lengths.
int[][] jagged = new int[3][];
jagged[0] = new int[2];
jagged[1] = new int[4];
jagged[2] = new int[3];
This creates rows with different column sizes.
Real-World Analogy
Think of a cinema hall: each row (array) can have a different number of seats (columns). That’s exactly how jagged arrays work.
Performance and Memory Implications
- Multidimensional arrays are stored as references to arrays, so memory is allocated per row.
- Jagged arrays can save memory if your dataset has uneven row lengths.
- Access time is O(1), but initialization cost grows with size.
Best Practices
- Use jagged arrays for irregular datasets to optimize memory.
- Always check for
NullPointerExceptionwhen working with dynamically allocated rows. - Prefer enhanced
forloops for readability.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Mixing dimensions: Avoid using mismatched row sizes unless intentional (jagged).
- Uninitialized rows: Always initialize sub-arrays in jagged arrays.
- Confusing length properties:
array.lengthgives rows;array[i].lengthgives columns.
Interview Questions
-
Q: How are multidimensional arrays stored in Java? A: As arrays of arrays, making them reference-based, unlike C/C++.
-
Q: Difference between rectangular and jagged arrays? A: Rectangular arrays have equal-length rows, jagged arrays have variable lengths.
-
Q: When should you use jagged arrays? A: When data rows vary in size to save memory and optimize performance.
Conclusion
Multidimensional arrays are a powerful feature in Java, enabling structured data storage. Understanding their declaration, initialization, and memory behavior is critical for writing optimized code.
FAQ
Q: Can a multidimensional array be null?
A: Yes, you can declare without initializing. Accessing it before initialization throws NullPointerException.
Q: Are multidimensional arrays thread-safe?
A: No, you must handle synchronization manually.