Loops in Java – for, while, do-while, and Enhanced for-loop
Loops are fundamental in Java programming. They allow you to execute a block of code repeatedly until a condition is met, making programs efficient and dynamic.
🔍 Why Loops are Important?
- Automate repetitive tasks.
- Reduce code duplication.
- Essential for working with arrays, collections, and algorithms.
- Widely used in real-world Java projects and interviews.
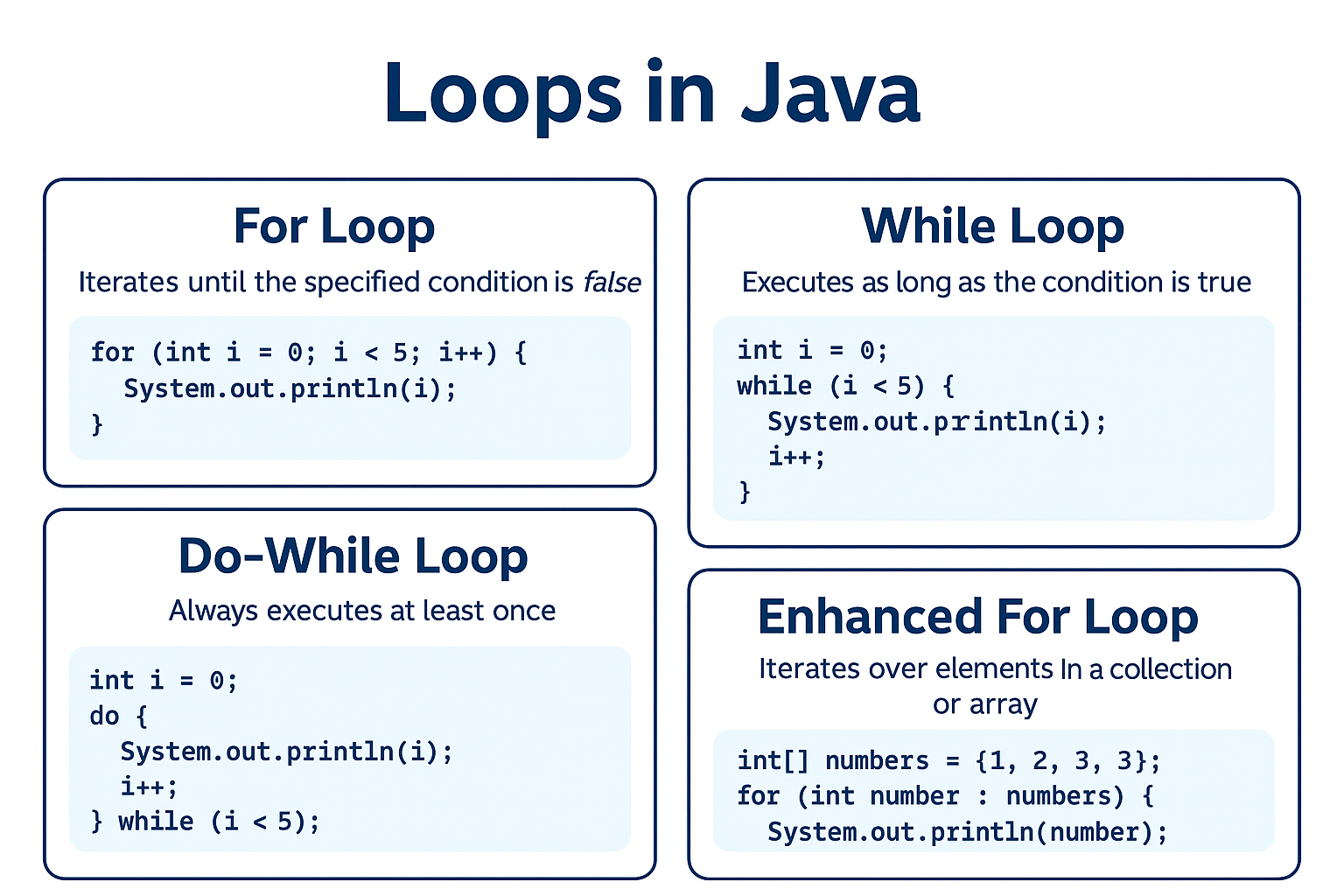
✅ for Loop
The for loop is used when the number of iterations is known beforehand.
✅ Syntax:
for(initialization; condition; update) {
// Code block
}
✅ Example:
for(int i = 1; i <= 5; i++) {
System.out.println("Iteration: " + i);
}
✅ while Loop
The while loop is used when the number of iterations is unknown and depends on a condition.
✅ Syntax:
while(condition) {
// Code block
}
✅ Example:
int count = 1;
while(count <= 5) {
System.out.println("Count: " + count);
count++;
}
✅ do-while Loop
The do-while loop executes the block at least once, even if the condition is false.
✅ Syntax:
do {
// Code block
} while(condition);
✅ Example:
int num = 1;
do {
System.out.println("Number: " + num);
num++;
} while(num <= 5);
✅ Enhanced for Loop (for-each)
Introduced in Java 5, the enhanced for loop simplifies iteration over arrays and collections.
✅ Example:
int[] numbers = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5};
for(int n : numbers) {
System.out.println("Value: " + n);
}
🔄 Performance & When to Use
- for loop: Best for indexed iterations or when count is known.
- while loop: Ideal when condition-driven repetition is needed.
- do-while: Use when block must execute at least once.
- enhanced for: Best for arrays and collections without index operations.
🚫 Common Mistakes
- Infinite loops due to missing update or wrong condition.
- Modifying a collection inside an enhanced for-loop.
- Using while when index-based iteration is required.
💡 Tips & Best Practices
- Use descriptive loop variables.
- Keep loop logic minimal and avoid heavy operations inside.
- Use
breakandcontinuewisely to control flow. - Prefer enhanced for-loop for read-only iteration of collections.
🧠 Interview Relevance
-
Q: Difference between for and while loop?
-
A: for is count-controlled; while is condition-controlled.
-
Q: When to use enhanced for loop?
-
A: When iterating through arrays or collections without modifying them.
🧩 Java Version Relevance
| Java Version | Feature |
|---|---|
| Java 1.0 | Introduced for, while, do-while loops |
| Java 5 | Added enhanced for loop for collections and arrays |
✅ Summary
- for: Use for fixed iterations.
- while: Use for condition-driven iterations.
- do-while: Ensures at least one execution.
- enhanced for: Simplifies array and collection traversal.