Java Labels – Labeled Loops and Their Usage
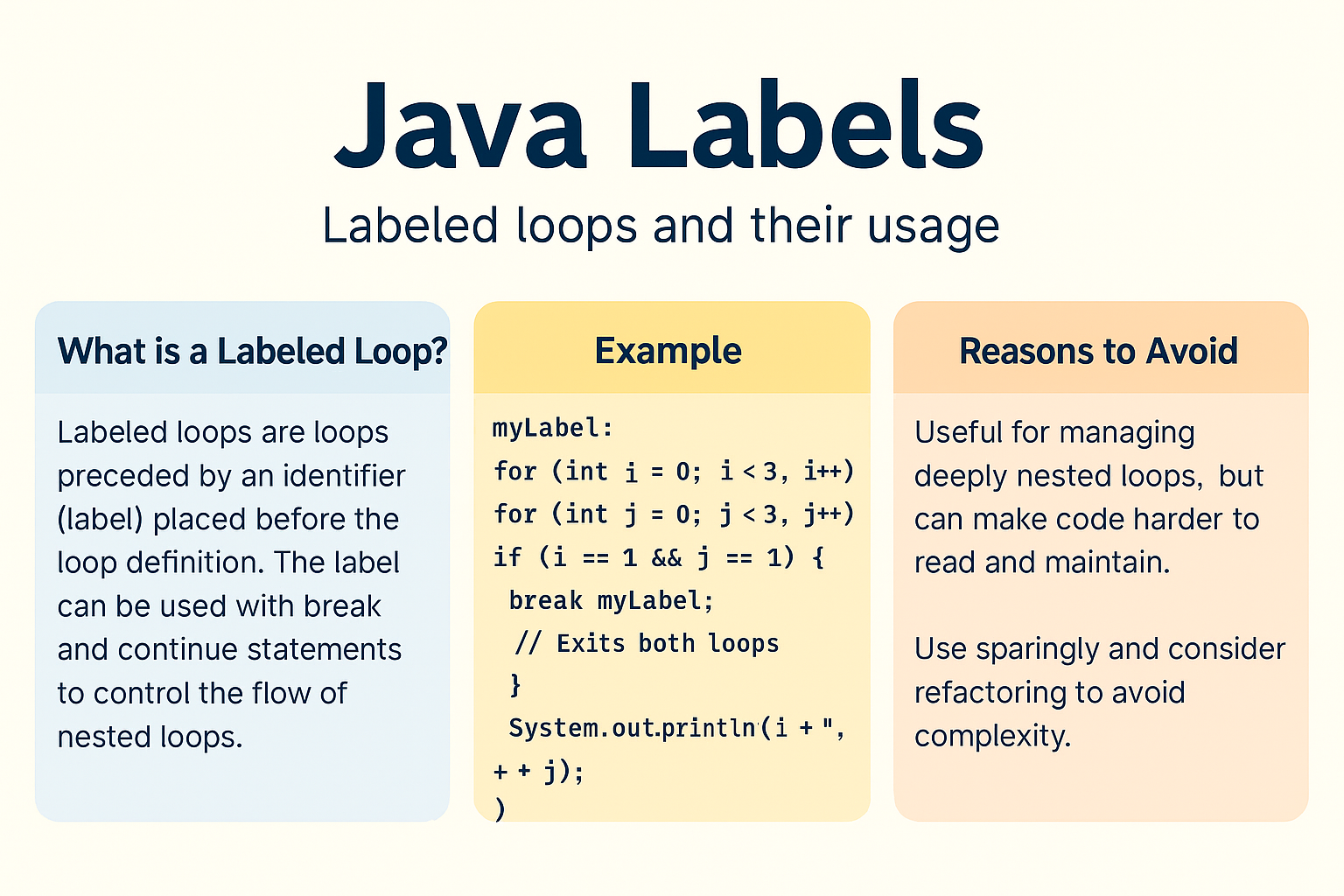
In Java, labels are identifiers followed by a colon (:) used to mark a block of code, commonly loops. Labeled loops are particularly useful when working with nested loops where standard break or continue is not enough.
🔍 Why Use Labels?
- Provide better control in nested loops.
- Allow breaking or continuing specific outer loops.
- Improve code readability in complex iterations.
✅ What is a Java Label?
A label is a simple name followed by a colon (:) placed before a loop or block. It’s used in conjunction with break or continue.
✅ Syntax:
labelName:
for(initialization; condition; update) {
// code
}
✅ Example: Breaking an Outer Loop
outerLoop:
for(int i = 1; i <= 3; i++) {
for(int j = 1; j <= 3; j++) {
if(i == 2 && j == 2) {
break outerLoop; // Breaks out of both loops
}
System.out.println(i + " " + j);
}
}
Output:
1 1
1 2
1 3
2 1
✅ Example: Continuing an Outer Loop
outerLoop:
for(int i = 1; i <= 3; i++) {
for(int j = 1; j <= 3; j++) {
if(j == 2) {
continue outerLoop; // Skips to next iteration of outer loop
}
System.out.println(i + " " + j);
}
}
Output:
1 1
2 1
3 1
🔄 Performance & When to Use
- Labels are not commonly used and should be reserved for complex nested loops.
- Overuse can make code harder to read.
- Prefer refactoring into methods instead of relying on labeled breaks for deeply nested logic.
🚫 Common Mistakes
- Using labels without break/continue (they serve no purpose).
- Overusing labels where a refactored method would make code cleaner.
- Placing labels before non-loop blocks (valid, but rarely useful).
💡 Tips & Best Practices
- Use descriptive names for labels.
- Limit nested loops to maintain readability.
- Consider using methods instead of labels when possible.
🧠 Interview Relevance
-
Q: Can labels be used with switch statements?
-
A: No, labels are meant for loops and blocks, not switches.
-
Q: Are labels in Java like goto?
-
A: No, Java doesn’t support goto. Labels only work with break/continue, not arbitrary jumps.
🧩 Java Version Relevance
| Java Version | Feature |
|---|---|
| Java 1.0 | Introduced labeled loops with break and continue |
✅ Summary
- Labels provide control for nested loops.
- Use
break label;to exit outer loops. - Use
continue label;to skip to next iteration of outer loops. - Avoid overuse; prefer method refactoring.