Java Operators (Extended) – Bitwise, Logical, Ternary, and Assignment Operators in Detail
Operators in Java are special symbols that perform operations on variables and values. While arithmetic and relational operators are common, understanding bitwise, logical, ternary, and assignment operators is critical for efficient and optimized Java programs.
🔍 Why Learn These Operators?
- Used extensively in conditional logic, low-level programming, memory optimization, and data manipulation.
- Frequently asked in Java interviews for both beginners and experienced developers.
- Essential for writing high-performance code, especially in competitive programming and backend systems.
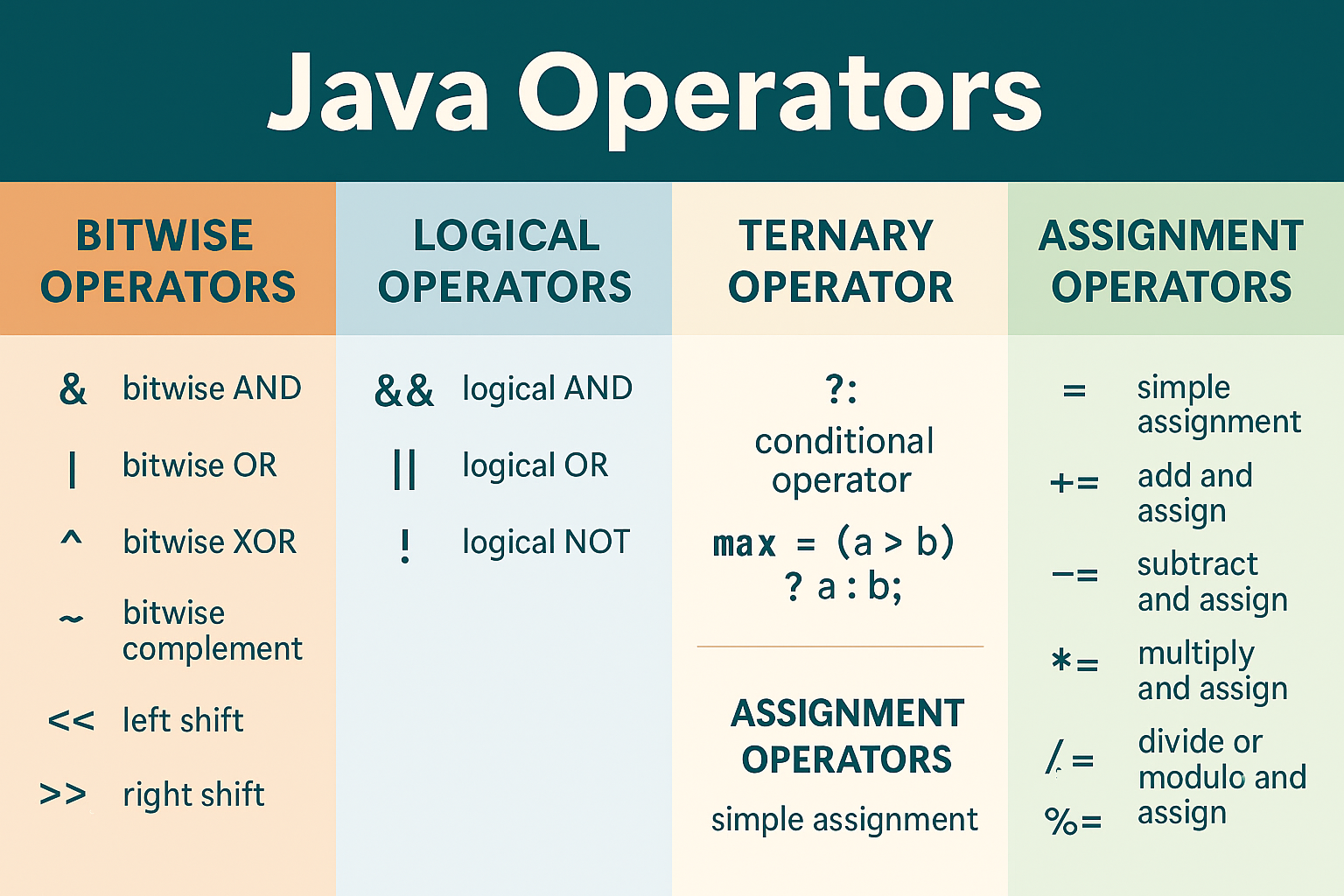
🔢 Bitwise Operators in Java
Bitwise operators work directly on bits. They are commonly used for encryption, compression, and low-level tasks.
📜 List of Bitwise Operators:
| Operator | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
& |
AND: Sets bit to 1 if both bits are 1 | 5 & 3 → 1 |
| |
OR: Sets bit to 1 if any bit is 1 | 5 | 3 → 7 |
^ |
XOR: Sets bit to 1 if only one bit is 1 | 5 ^ 3 → 6 |
~ |
Complement: Inverts bits | ~5 → -6 |
<< |
Left shift | 5 << 1 → 10 |
>> |
Right shift | 5 >> 1 → 2 |
>>> |
Unsigned right shift | -5 >>> 1 |
✅ Example:
public class BitwiseExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a = 5; // 0101
int b = 3; // 0011
System.out.println(a & b); // Output: 1
System.out.println(a | b); // Output: 7
System.out.println(a ^ b); // Output: 6
}
}
🔗 Logical Operators in Java
Logical operators are used to combine conditional expressions.
| Operator | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
&& |
Logical AND | (a > 0 && b > 0) |
|| |
Logical OR | (a > 0 || b > 0) |
! |
Logical NOT | !(a > b) |
✅ Example:
public class LogicalExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a = 10, b = 20;
System.out.println(a > 0 && b > 0); // true
System.out.println(a > b || b > 5); // true
}
}
❓ Ternary Operator
The ternary operator is a concise way to perform conditional assignments.
Syntax:
variable = (condition) ? valueIfTrue : valueIfFalse;
✅ Example:
public class TernaryExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int age = 18;
String result = (age >= 18) ? "Adult" : "Minor";
System.out.println(result);
}
}
📌 Best Use: Replace short if-else conditions for readability.
📝 Assignment Operators
Assignment operators are used to assign values and perform shorthand operations.
| Operator | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
= |
Assign value | a = 5; |
+= |
Add and assign | a += 2; // a = a + 2 |
-= |
Subtract and assign | a -= 2; |
*= |
Multiply and assign | a *= 2; |
/= |
Divide and assign | a /= 2; |
%= |
Modulus and assign | a %= 2; |
✅ Example:
public class AssignmentExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a = 10;
a += 5;
a *= 2;
System.out.println(a); // Output: 30
}
}
🚫 Common Mistakes
- Confusing
&&and&in logical operations. - Using
=instead of==in conditionals. - Forgetting precedence of bitwise operators.
💡 Tips & Best Practices
- Use bitwise operators in performance-critical code (e.g., masks).
- Prefer ternary operators for short, simple conditions.
- Always use parentheses to clarify precedence in complex expressions.
🧠 Interview Relevance
-
Q: Difference between
&and&&? -
A:
&evaluates both operands,&&performs short-circuit evaluation. -
Q: When to use
>>>? -
A: For unsigned bit manipulation in numbers.
🧩 Java Version Relevance
| Java Version | Feature |
|---|---|
| Java 1.0 | All these operators introduced |
| Java 7+ | Improved unsigned right shift behavior |
✅ Summary
- Bitwise operators for low-level bit manipulation.
- Logical operators for boolean conditions.
- Ternary operator for concise conditional assignment.
- Assignment operators for shorthand updates.