Java Comments and Documentation: Writing Clean, Maintainable Code
Comments and documentation are critical for writing readable and maintainable Java code. They help developers understand the intent behind code, improve collaboration, and allow automatic generation of API documentation.
🔍 What Are Comments in Java?
Comments are non-executable statements in the source code that serve as notes for developers. The compiler ignores them.
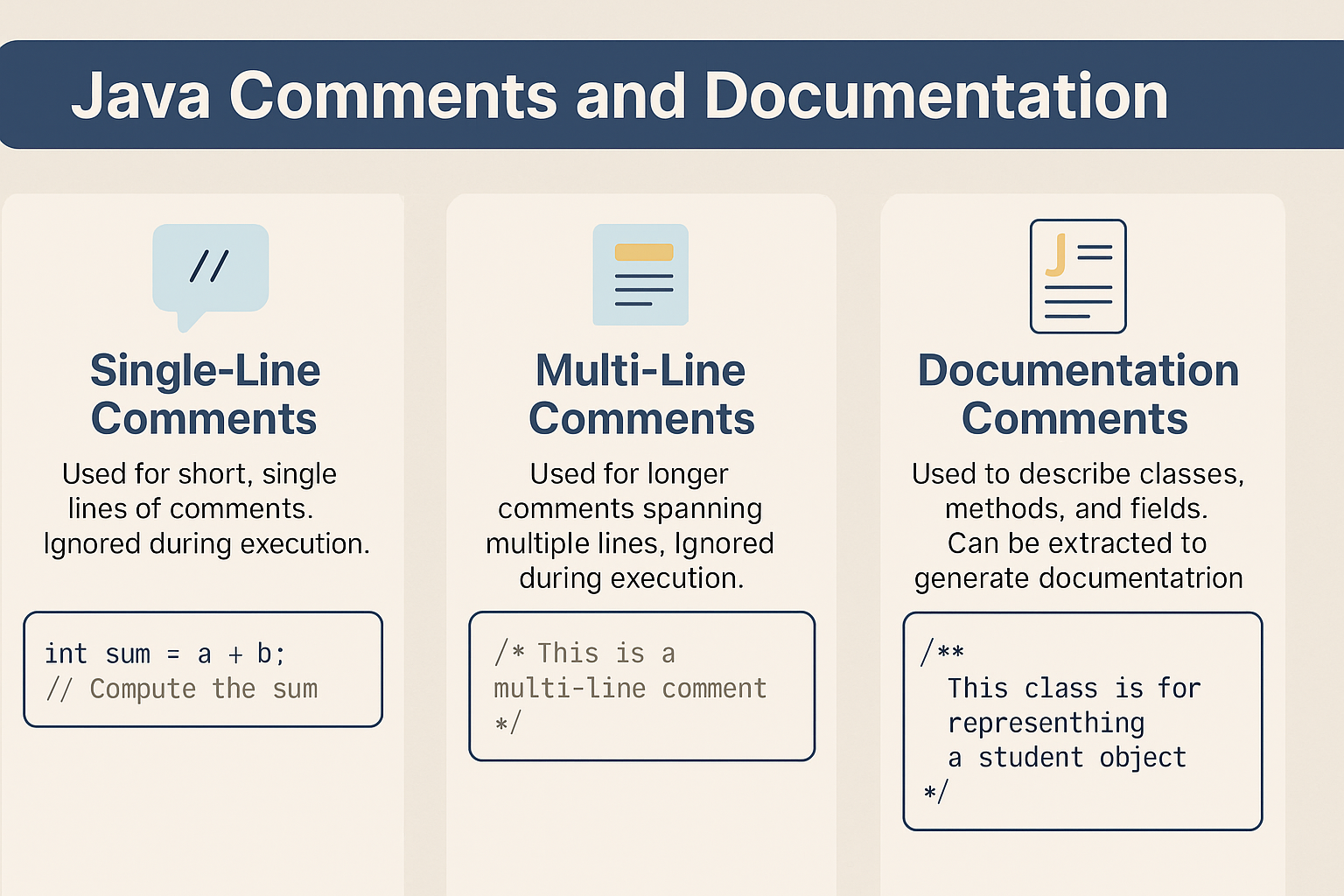
Types of Java Comments:
- Single-Line Comments (
//) - Multi-Line Comments (
/* ... */) - Javadoc Comments (
/** ... */)
✍️ Single-Line Comments
Used for brief explanations or annotations.
public class HelloWorld {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Print a greeting message
System.out.println("Hello, World!");
}
}
✅ Best Practice: Keep them short and relevant.
📄 Multi-Line Comments
Useful for larger explanations or temporarily disabling code.
/*
This class demonstrates the use of multi-line comments.
It can span multiple lines.
*/
public class Calculator {
public int add(int a, int b) {
return a + b; // simple addition
}
}
⚠️ Anti-Pattern: Avoid commenting obvious code like i++ // increment i by 1.
📚 Javadoc Comments
Special comments used to generate HTML documentation.
/**
* This class provides math utilities.
* @author John
* @version 1.0
*/
public class MathUtils {
/**
* Adds two numbers.
* @param a first number
* @param b second number
* @return sum of a and b
*/
public int add(int a, int b) {
return a + b;
}
}
Generate docs using:
javadoc MathUtils.java
✅ Best Practice: Always use Javadoc for public APIs.
🆚 Comparison of Comment Types
| Feature | Single-Line | Multi-Line | Javadoc |
|---|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Short notes | Detailed explanations | API documentation |
| Compiler Behavior | Ignored | Ignored | Processed by javadoc tool |
| Use-Case | Inline hints | Block comments | Public API docs |
💡 Tips and Best Practices
- Write comments to explain why, not what.
- Keep comments updated; outdated comments are worse than none.
- Use Javadoc for libraries and APIs.
- Avoid excessive commenting that clutters code.
🚫 Common Mistakes
- Commenting obvious logic (
x = x + 1; // adds 1 to x). - Using comments as a substitute for clear variable/method names.
- Forgetting to update comments after refactoring.
📌 Performance Impact
Comments have no runtime performance cost since they are stripped at compile time.
🧩 Java Version Relevance
| Java Version | Changes Related to Comments |
|---|---|
| Java 1.2 | Introduced Javadoc tags like @since |
| Java 5 | Added @deprecated tag enhancements |
| Java 8+ | Supports Javadoc with lambda and default methods |
✅ Summary
- Use comments for readability and intent.
- Prefer Javadoc for reusable APIs.
- Keep them updated and meaningful.